Vaccine Preventable
Diseases
Did you know the very first vaccine was developed in the late 1700’s? Edward Jenners, an English physician, created the smallpox vaccine, our first successful vaccine. Smallpox is currently the only human disease to date that has been eradicated (the permanent elimination of a disease) (History of smallpox vaccination, World Health Organization)
Now in 2024, our past is becoming our current trends! While flip phones, record players and 80’s & 90’s music are back in, many of us do not even recognize the diseases below. That is because of vaccines! Learn about the vaccine preventable diseases that are still in our day to day lives, and the vaccine you can receive to protect yourself. Vaccination on time is the best defense against these diseases and the only way to see more vaccine preventable diseases become a think of the past, where they belong!
Together, we can help our children and community experience the good parts of our past!
Vaccine Preventable Diseases
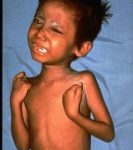
Chickenpox (Varicella)
What is it? A highly contagious disease caused by a virus, it presents as an itchy skin rash.
Symptoms:
Children: Usually, a rash is the first sign in children; it appears as red-raised spots that turn into itchy, fluid-filled blisters.
Adults: May have fatigue and fever 1-2 days before the rash.
How is it spread? Through direct contact with fluid from blisters or through the air when someone with chickenpox coughs or sneezes.
Vaccine: Varicella vaccine or MMRV (Measles, Mumps, Rubella and Varicella)
Where To Find Vaccines Near You >
COVID
What is it? A respiratory infection caused by a virus named SARS-CoV-2 that can progress to severe pneumonia (lung infection).
Symptoms:
You may experience sudden fever or chills, cough, shortness of breath, loss of taste or smell, or be asymptomatic.
How is it spread? When an infected person breathes out droplets or very small particles to other people who can breathe it in or have it land on their eyes, nose, or mouth.
Vaccine: COVID-19
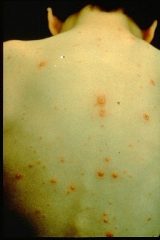
Diphtheria
What is it? A bacterial disease that affects the tonsils, throat, nose, and sometimes skin
Symptoms:
Sore throat, low-grade fever, and enlarged lymph nodes in the neck. Diphtheria can also make it difficult to swallow and breathe. Skin lesions may be painful, swollen, and reddened.
How is it spread? Through close contact with the discharge from an infected person’s eyes, nose, throat, or skin.
Vaccine: DtaP, Td, Tdap
Where To Find Vaccines Near You >
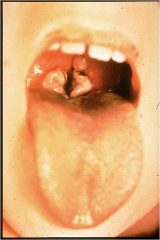
Flu (Influenza)
What is it? A respiratory disease that attacks the nose, throat, and lungs. It can cause mild to severe illness and, can lead to death.
Symptoms:
Influenza symptoms come on quickly and include fever, dry cough, sore throat, headache, extreme tiredness, stuffed-up nose, and body aches. These symptoms can be severe and put you in bed for several days.
How is it spread? Through the sneezing or coughing of an infected person. Experts also think you can get the flu by touching a surface with flu germs on it and then touching your mouth or nose.
Vaccine: TIV, LAIV
Where To Find Vaccines Near You >

Hepatitis A
What is it? A virus that attacks the liver.
Symptoms:
Symptoms may range from mild to severe and can include an abrupt onset of fever, fatigue, poor appetite, nausea, stomach pain, dark-colored urine, and jaundice (a yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes).
How is it spread? It’s spread by putting something in the mouth that has been contaminated with the stool of a person with hepatitis A.
Vaccine: Hep A
Where To Find Vaccines Near You >
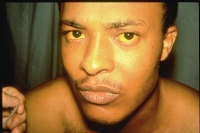
Hepatitis B
What is it? A virus that attacks the liver.
Symptoms:
Many people have no symptoms. Early symptoms are mild fever, headache, muscle aches, fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Later symptoms may include dark coffee-colored urine rather than dark yellow, clay-colored stools, abdominal pain, and yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice).
How is it spread? Direct contact with blood or other body fluids of infected people can be spread from a pregnant woman to her baby during childbirth.
Vaccine: Hep B
Where To Find Vaccines Near You >
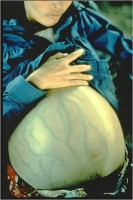
Haemophilus influenzae Type B (Hib)
What is it? A type of bacteria found in the nose and throat of children and adults could lead to brain damage or death.
Symptoms:
Causes a variety of illnesses, including meningitis (inflammation of the coverings of the spinal column and brain), bacteremia (infection of the blood), pneumonia (infection of the lungs), and septic arthritis (infection of the joints). Some people can carry the bacteria in their bodies but do not become sick.
How is it spread? Through the sneezing or coughing of an infected person.
Vaccine: Hib
Where To Find Vaccines Near You >
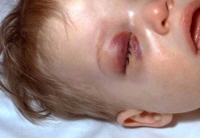
Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
What is it? A common virus that infects the skin, particularly the genital area. It is the most common sexually transmitted disease in the US and can cause cervical cancer.
Symptoms:
Most of the time, there are no symptoms, and most HPV infections go away on their own. Some high-risk HPV types will cause an ongoing (chronic) infection in the cervix. This causes abnormal Pap smears. Chronic HPV infection can lead to cancer, especially cervical cancer. HPV can cause genital warts, which can be uncomfortable and irritating and can reoccur. Sometimes, genital warts spread to a baby during birth and infect the baby’s lungs and airway.
How is it spread? There are over 100 types of human papillomaviruses, and about 40 of them are spread through sexual contact.
Vaccine: HPV
Where To Find Vaccines Near You >
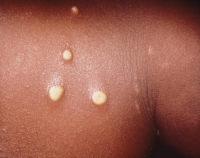
Measles
What is it? A virus also called rubeola. It can lead to hearing loss, breathing problems, pneumonia, brain damage, and death.
Symptoms:
Fever, runny nose, cough, loss of appetite, watery/mattering eyes, and a rash. The rash usually lasts 5-6 days and begins at the hairline, moves to the face and upper neck, and proceeds down the body. It generally takes 8-12 days from exposure to the first symptom, which is usually fever. A measles rash usually appears 2-3 days after the fever begins.
How is it spread? Through the air by infectious droplets and is highly contagious.
Vaccine: MMR, MMRV
Where To Find Vaccines Near You >
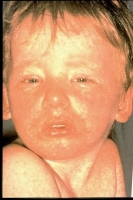
Meningococcal
What is it? It can include a variety of serious clinical illnesses, including meningitis (infection of the lining of the spinal cord), bacteremia (bacteria in the blood), and rarely, pneumonia (infection of the lungs). Children and young adults are most often affected by this disease. It can cause severe illness and death.
Symptoms:
Fever, vomiting, headache, stiff neck, extreme sleepiness, confusion and irritability, and lack of appetite; sometimes, a rash or seizures occur.
How is it spread? Through nose and throat secretions (e.g., coughing, sneezing); in turn it is more common in household and childcare settings. Of the people who carry the bacteria in the nose and throat, only a very few will develop the disease. However, people who carry the bacteria can sometimes carry it to others, who will, in turn, become sick.
Vaccine: Men ACWY, Men B
Where To Find Vaccines Near You >
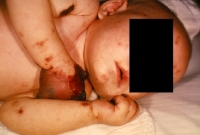
Mpox (formerly known as monkeypox)
What is it? It is a rare disease that commonly affects rats and monkeys but can affect humans.
Symptoms:
Rash that may look like pimples or blisters on or near the genitals or anus and other areas like the hands, feet, chest, face, or mouth. Symptoms usually start 5-21 days after exposure.
How is it spread? Close, personal contact with infected animals or people and through contact with clothing an infected person has touched.
Vaccine: JYNNEOS
Where To Find Vaccines Near You >
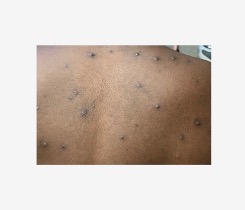
Mumps
What is it? A very contagious infection of one or more of the salivary glands. These glands are on either side of the face, below the ears. In some cases, it can lead to hearing loss, swelling of the brain and spinal cord, and brain damage.
Symptoms:
Severe swelling and soreness of the cheeks and jaw. It usually starts with neck or ear pain, loss of appetite, tiredness, headache, and low fever. About a third of persons infected have no symptoms.
How is it spread? Through direct contact with saliva and discharges from the nose and throat of infected persons. Coughing, sneezing, or even talking can spread mumps.
Vaccine: MMR, MMRV
Where To Find Vaccines Near You >
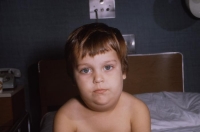
Pertussis (Whooping Cough)
What is it? A disease that affects the lungs. It causes long spells of coughing that make it hard for a child to eat, drink, and breathe. It can lead to pneumonia, seizures, and death.
Symptoms:
The first symptoms of whooping cough are like those of a common cold: runny nose, sneezing, mild cough, and low-grade fever. After about 1 to 2 weeks, the dry, irritating cough evolves into coughing spells, which can last for more than a minute, and the child may turn red or purple.
How is it spread? Through the air by infectious droplets such as sneezing or coughing; highly contagious.
Vaccine: DtaP, DTP, Tdap
Where To Find Vaccines Near You >
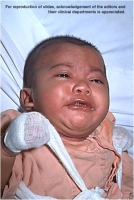
Polio
What is it? A virus that lives in the intestinal tract and sometimes in the throat. It can cause lifelong paralysis and deformity.
Symptoms:
Fever, fatigue, headache, vomiting, stiffness in the neck, and pain in the limbs. However, up to 95 percent of all persons infected with polio will have no symptoms.
How is it spread? Through contact with the stool of an infected person (for instance, by changing diapers). Polio virus must be swallowed to cause infection.
Vaccine: IPV
Where To Find Vaccines Near You >
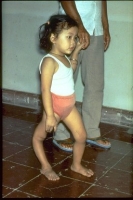
RSV (Respiratory Syncytial Virus)
What is it? It is a common respiratory virus that usually causes mild, cold-like symptoms. Infants and older adults are more likely to develop severe RSV and need hospitalization.
Symptoms:
Usually appear 4-6 days after infection and include runny nose, cough, sneezing, fever, or wheezing.
How is it spread? It spreads when an infected person coughs or sneezes or you come into contact with a contaminated surface and touch your mouth, nose, or eyes.
Vaccine: RSV
Where To Find Vaccines Near You >
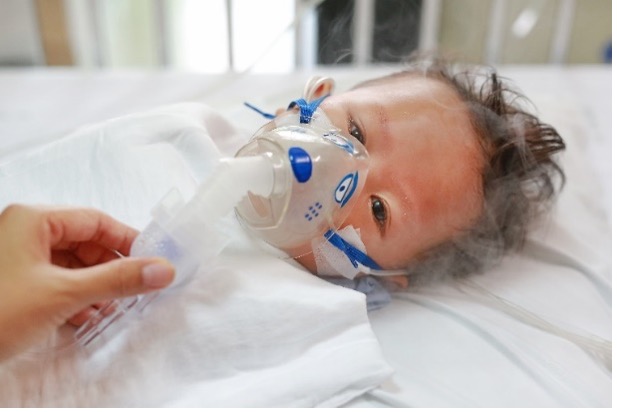
Rubella (German Measles)
What is it? A virus that causes fever and rash on the face and neck. It can lead to miscarriage or congenital disabilities if contracted during pregnancy.
Symptoms:
Rash, low-grade fever, cough, and swollen glands behind the ears and neck. The rash generally appears first on the face and moves from head to foot. Up to half of all people infected with rubella do not have symptoms.
How is it spread? When an infected person coughs or sneezes near you or by touching infected fluid and then touching your eyes, nose, or mouth.
Vaccine: MMR, MMRV
Where To Find Vaccines Near You >
Tetanus (Lockjaw)
What is it? A disease caused by bacteria that affects the body’s muscles and nerves; causes severe muscle spasms, breathing, and heart problems, and may lead to death.
Symptoms:
Muscle spasms in the jaw, difficulty swallowing, and stiffness or pain in the neck, shoulders, or back muscles. The spasms can spread to the abdomen, upper arms, and thigh muscles.
How is it spread? It cannot be spread from person to person. The only way to get tetanus is from a skin wound that becomes contaminated by the tetanus bacteria, which is often found in soil.
Vaccine: DT, DtaP, Td, Tdap
Where To Find Vaccines Near You >